Fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine are classified based upon the pattern of injury. The three major types of spine fracture patterns are flexion, extension and rotation.
Flexion fracture pattern
Compression fracture – the front (anterior) of the vertebra breaks but the back (posterior) part does not. This is a stable fracture.
Axial burst fracture – both front and back parts of the vertebra breaks.
Extension fracture pattern
Flexion/distraction (Chance) fracture – the vertebra is literally pulled apart (distraction). Circumstance that might cause such a fracture is head-on car crash wearing a seat belt.
Rotation Fracture Pattern
Transverse process fracture – rotational movement or extreme lateral bending could result in this vertebra fracture. However this fracture is typically uncommon. This is a stable fracture.
Fracture-dislocation – a vertebra slides off an adjacent vertebra and is hence displaced. This is an unstable injury causing spinal cord compression.
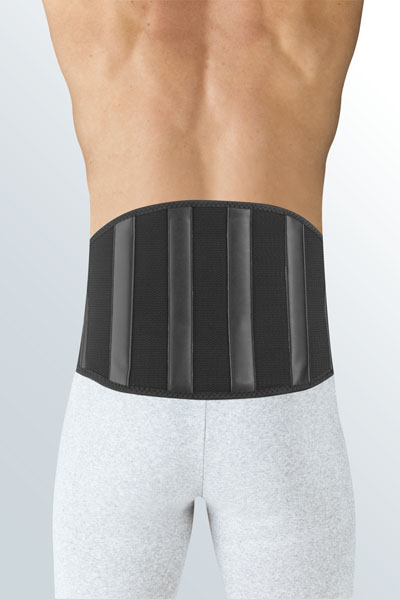
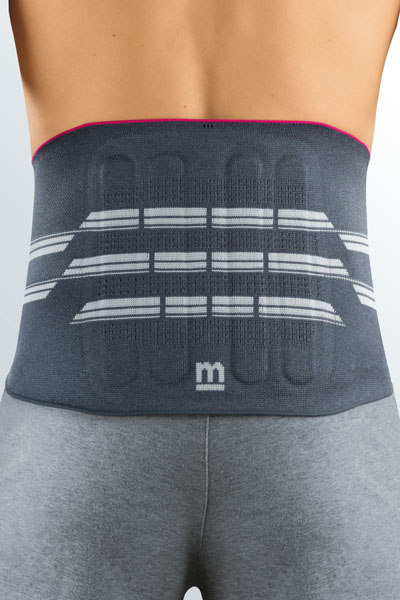
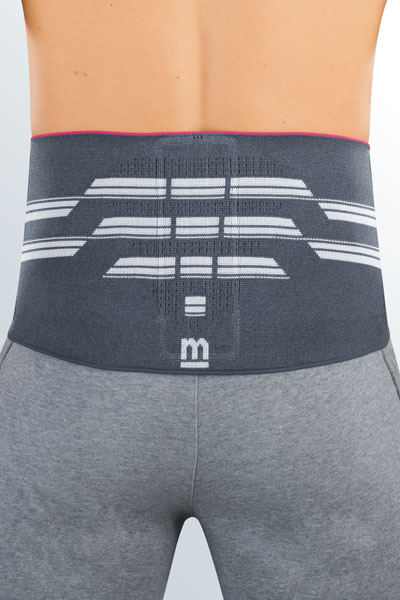
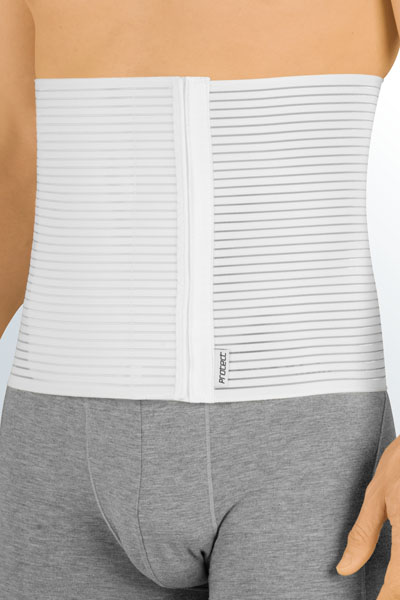
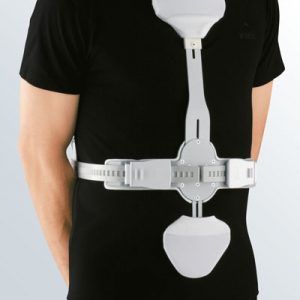
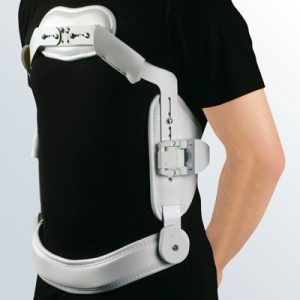
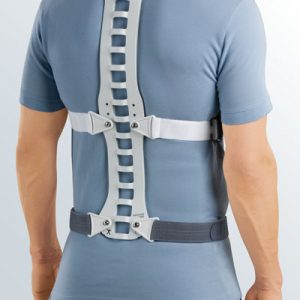
Medical tip
Orthopaedic supports or braces advised against stable vertebral fractures are
Medical supports and braces are prescribed by the doctor if required, and the patients are measured for the correct fit by specialist medical retailers (e.g. surgical appliance dealers): the user’s relevant measurements are taken so that an exact anatomical fit is achieved.